What hair restoration treatments are available?
There are a number of over-the-counter treatments, prescription medications, and surgeries that can help men and women combat hair loss. Non-surgical approaches tend to be most successful in slowing down hair loss and stimulating new growth when they are started early.
Once your hair follicles have stopped producing fresh hair and become dormant for an extended period of time (usually about two years) it can be difficult, if not impossible, to reactivate them. Once follicles go dormant, surgery may be the only viable option.
Prescription medications
If over-the-counter methods have not been successful, your physician may prescribe finasteride – also known as Proscar or Propecia. This prescription medication is FDA-approved to slow hair loss and stimulate regrowth in the majority of men.
For women, Minoxidil (Rogaine) is approved to treat female pattern baldness. Some physicians also prescribe Spironolactone to block the male hormones that can cause hair loss in women.
Hair transplantation
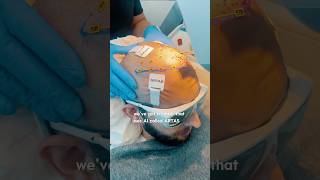
Hair transplant surgery can restore hair to thinning or balding areas of the scalp. It’s done via two distinct methods: follicular unit transplant or follicular unit extraction.
With follicular unit transplant, your surgeon will remove a strip of skin with hair follicles from the back of the scalp. We will then remove hair follicles from that skin and transplant them to balding sites.
With follicular unit extraction, we will remove individual hair follicles from the back of the scalp without removing any skin. Those individual hair follicles will then be inserted into the balding areas to regrow naturally.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) may boost natural hair growth by increasing blood supply to the follicles. First, we will draw blood from your arm and put it into a centrifuge to separate the PRP from the rest of your blood. We will then place the PRP in a syringe and inject it into areas of the scalp that will benefit from improved hair growth.